Uterine Fibroids
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. These smooth muscle tumors vary in size and number and can occur during a woman’s reproductive years. While many women may not experience symptoms, fibroids can sometimes cause significant discomfort and complications.
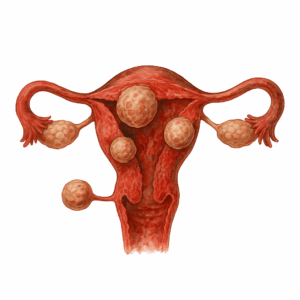
Common Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
While some women with fibroids remain asymptomatic, others may experience a range of symptoms that affect quality of life such as infertility, complications during pregnancy, and pain during intercourse.
Other common symptoms include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Pain during intercourse
- Lower back pain
- Difficulty getting pregnant
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
The exact cause of fibroids remains unknown. However, research suggests that each tumor originates from a single abnormal muscle cell in the uterus, which then multiplies rapidly under the influence of estrogen—a hormone that plays a key role in stimulating fibroid growth. Uterine fibroids are more common in women between ages 30 and 50 and more prominent in African American’s. Women are typically at risk of developing fibroids if:
- They have a family history of fibroids
- They are overweight
- Their diet is high in red meat
- They have high blood pressure
Schedule Your Appointment Today
Treatment Options
Medications for Uterine Fibroids
Anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids while also providing effective pain relief. This conservative treatment approach is often recommended for women who experience mild or occasional pelvic pain or discomfort due to fibroids.
Hormonal treatments may include:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists: These medications lower estrogen levels and induce a temporary “medical menopause,” which helps shrink fibroids. They are often prescribed to stop menstrual bleeding prior to surgery or to improve low blood counts caused by heavy bleeding. Due to potential side effects, GnRH agonists are typically used for no longer than one year. Once the medication is discontinued, its effects are reversible.
- Oral contraceptives (including the pill, patch, or vaginal ring): These can help manage fibroid-related bleeding by regulating hormone levels and stabilizing the endometrial lining.
- Progesterone-based therapies: Available in the form of pills, injections, implants, or an intrauterine device (IUD), these treatments can also effectively reduce heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
Minimally Invasive Procedures for BPH
For men who don’t respond to medications or prefer to avoid long-term drug use, minimally invasive BPH treatments offer excellent results with faster recovery and fewer side effects than traditional surgery.
Minimally Invasive Options:
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): A minimally invasive procedure used to shrink fibroids by blocking their blood supply. Performed by an interventional radiologist under X-ray guidance, UAE causes fibroids to shrink over time due to lack of nourishment.
- Myomectomy: a procedure during which the fibroids are removed but the uterus stays intact. This approach is recommended for women who want to preserve their fertility.
